Government initiatives to boost Indian electronics sector

Business Development
292 week ago — 9 min read
In our previous article on the electronics industry in India, we examined some of the growth drivers and key trends in this sector.
The National Policy on Electronics (NPE) envisions India as a global hub for Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) by encouraging and driving capabilities in the country for developing core components and creating an enabling environment for the industry to compete globally.
In this article we examine some of the schemes, initiatives and policies by the government to boost the electronics sector in India.
Schemes
M-SIPS scheme:
To offset disability and attract investments in electronic manufacturing, Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme (M-SIPS) was notified on 27 July 2012. The scheme is available for both new projects and expansion projects. Under M-SIPS, 25% of capex is eligible for subsidy (20% for units in Special Economic Zones) for all investments made in manufacturing of ESDM (electronic system design and manufacturing) products. For some of the high capital investment projects like fabs, it provides for reimbursement of Central Taxes and Duties. The incentives are provided on reimbursement basis. Units all across the manufacturing value chain are covered under the scheme. For each of the product category, an investment threshold is prescribed which an applicant has to incur for getting eligible for incentives. The investment threshold varies from INR 1 crore to INR 5,000 crores depending upon a type of project.
The scheme was initially opened for three years till 26 July 2015 but was later extended up to 26 July 2020 post amendments dated 3 August 2015.
For more details click here.
Electronic Manufacturing Clusters (EMCs)
This scheme provides financial assistance for creating world-class infrastructure for electronics manufacturing units. India is developing various Electronic Manufacturing Clusters to achieve the vision of ‘Net Zero Import By 2020’. The assistance for the projects for setting up of Greenfield Electronics Manufacturing Clusters is 50% of the project cost subject to a ceiling of INR 50 crore for 100 acres of land. For larger areas, pro-rata ceiling applies. For lower extent, the extent of support would be decided by the Steering Committee for Clusters (SCC) subject to the ceiling of INR 50 crore. For setting up of Brownfield Electronics Manufacturing Cluster, 75% of the cost of infrastructure, subject to a ceiling of INR 50 crore is provided. About 14 Greenfield EMC proposals have been given in principal approval, while two have been given final approval. Two common facility centres also have been accorded in principle approval.
For more details, click here.
Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS)
This scheme has notified certain products (includes AC parts and compressors, refrigerating equipment compressors, fully automatic washing machines, colour TV and STB for accessing internet) and markets for exports. These products, when exported to specified markets (category B countries), are offered 2% export subsidy. There is also provision for higher subsidy under the MEIS scheme for export items with high domestic content and value addition.
For more details, click here.
Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme for Electronics & IT
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology initiated this scheme with an objective to enhance the number of PhDs in Electronics System Design & Manufacturing (ESDM) and IT/IT Enabled Services (IT/ITES) sectors in the country. This scheme supports 3000 additional PhD (1500 in ESDM and 1500 in IT/ITES) and was approved in 2014. Out of 1500 additional PhDs in ESDM, 500 would be full time and 1000 would be part time. In addition, 100 PhDs (full-time) are to be supported by industry/State Government as a part of this scheme.
For more details, click here
Technology Incubation Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE) Scheme
This scheme was launched in 2008 and is valid up to 2020. As part of this scheme, financial assistance is provided to various higher learning institutions to strengthen their Technology Incubation Centres. Each TIDE centre would be given a financial support of up to INR 155 lakh as grant-in-aid, payable in instalments. Under this scheme, 27 TIDE centres and two virtual TIDE Centres are being supported at Institutes of Higher Learning that are located across the country.
For more details, click here
Scheme for Skill Development in ESDM for Digital India
Under the aegis of ‘Digital India’ programme, the department has approved a Scheme for “Skill Development in ESDM for Digital India” to cover all the States/UTs of the country in order to facilitate creation of an eco-system for development of ESDM sector in the entire country for facilitating skill development for 3,28,000 persons in ESDM sector at an outlay of INR 411 crore (approx.) This is in concurrence with the ‘Scheme for Financial Assistance to select States/UTs for Skill Development in Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) sector’ which is being implemented in 8 states.
For more details, click here.
Initiatives and Policies
Make in India
The government is driving reforms in IT and Electronics Manufacturing sector through initiatives like ‘Make in India’ and creating favourable policies to enable an investor-friendly environment. Electronic System Design and Manufacturing is one of the major sectors of ‘Make in India’.
Public Procurement (preference to Make in India) order was passed in 2017 by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology to promote manufacturing of goods and services in India. Under public procurement order, the government targeted 10 domestically manufactured electronic products for providing preference on the basis of prescribed domestic value addition, ranging from 40% to 70%. The category comprises of the following products: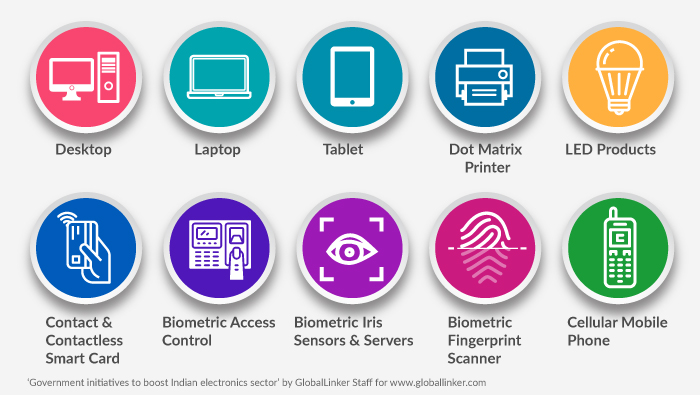
Digital India
The Digital India programme aims to transform India into a digitally enabled society and was launched in 2015. One of the nine pillars of Digital India is Electronics Manufacturing, with a focus on boosting the production of electronics in India. The focus areas comprise mobiles, fab-less design, set top boxes, VSATs, consumer and medical electronics, smart energy meters, smart cards and micro-ATMs.
Electronics Development Fund policy
This policy provides a framework to set up an Electronics Development Fund (EDF) as a Fund of Funds which will foster research and development (R&D) and innovation in technology sectors like electronics, IT and nano-electronics. EDF will support Venture Funds and Angel Funds, which will be professionally managed and are dedicated to these sectors.
For more details, click here.
R&D and IP Development:
Under the National Policy on Electronics, several initiatives are being taken to promote R&D and IP development in the ESDM sector.
The following initiatives are being taken in this direction:
- Setting up of Electronics Development Fund for promoting Venture Funds in ESDM area.
- Setting up of Incubators for supporting start-ups in ESDM sector.
- Development of Conditional Access System (CAS) for Set Top Boxes.
- Other projects as recommended by Working Group for this initiatives
For more details, click here.
Preferential Market Access (PMA)
This was launched in December 2013. Under this policy, the government provides the quota of minimum 30% for domestic players in procurement of electronic goods by government. The objective of PMA is to provide preference to domestically manufactured electronic goods that are procured by the government for its own use
Compulsory Registration Order (CRO)
Specified items must meet the specified safety standards under the Compulsory Registration Order (CRO) which has been brought into force from January 3, 2014. The CRO provides a framework to add other electronic items under this regime, thereby providing a quality barrier for unsafe and sub-standard electronic goods.
Posted by
GlobalLinker StaffWe are a team of experienced industry professionals committed to sharing our knowledge and skills with small & medium enterprises.
View GlobalLinker 's profile
Most read this week












Comments
Share this content
Please login or Register to join the discussion